Periodic Trend in Metal Reactivity Down a Group
Period - reactivity decreases as you go from left to right. The reactivity of Group 7 elements decreases down the group.

Discovering The Link Between Nutrition And Skin Aging Disease Disorders Cardiovascular
Period - reactivity decreases as you go from left to right.

. This makes it easier for the atom to give up the electron which increases its reactivity. The periodic trend in the solubility of alkaline earth metal compounds is that as one goes down a group it increases in activity. The electrons in the outer shell move further away from the nucleus as we go down the group and the attraction force between the electrons and the nucleus become weaker and weaker.
The bigger the atom. We can identify a trend in the melting points of group 1 elements. Reactivity is dependent on the classification of an element metals and non-metals as they both have differing periodic trends.
Down a group the reactivity and metallic character increases. The reactivity of metals increases further left along a period and further down a group. This happens because as you go down a group it is easier for electrons to be taken or given away resulting in high Chemical Reactivity.
What is the periodic trend for reactivity of metals. Group - reactivity increases as you go down a group In Non-metals Period - reactivity increases as you go from the left to the right. Within each group of metals reactivity increases as you go down the group.
Explore the trend in reactivity down group 1 of the Periodic Table by looking at the similarity of the physical and chemical properties of the alkali metals. Metal reactivity period trend decreases as you go across a period because though they still want to give away valence electrons they have more of them to get rid of which requires more energy non metal reactivity group trend. In metals down the group reactivity increases whereas in non metals down the group reactivity decreases.
Chemical Reactivity increases as you go down the group. Across a period the metallic character decreases. As the atomic radius increases down the group the delocalised electrons making up the metallic bond get further from the nucleus so the metallic bond gets weaker and easier to weaken as you go down the group.
As we go down the group the atom gets bigger. Use the solubility pattern observed for the known and unknown alkaline earth compounds in Part B to deduce the identity of the unknown alkaline earth metal. Keeping this in consideration what is the trend of reactivity of metals across a period.
Nov 17258 PM Reactivity Trends Metal reactivity increases down a group because as nuclear shielding increases and the nucleus hold on the valence electron weakens therefore it is easier to remove valence electrons. Therefore the attraction between the nucleus and the last electron gets weaker. Period - reactivity increases as you go from the left to the right.
Keeping this in view how does reactivity change as you go down a metal group. Nonmetal reactivity decreases down a group because the nucleus ability. As we go down the group the atom gets bigger.
Reactivity Trends Metal reactivity increases down a group because as nuclear shielding increases and the nucleus hold on the valence electron weakens therefore it is easier to remove valence electrons. 1620 demonstrate knowledge and understanding of how the reactivity down the group depends on the outer shell electrons of the atoms. Reactivity trends of the alkali metals.
Periodic Trends in Reactivity Introduction The structure of the periodic table is such that elements with similar properties are aligned vertically in columns called groups This leads to trends in properties such as electron affinity and atomic radius as one moves both down the periodic table within a specific group or as one moves horizon-. 1614 demonstrate knowledge and understanding of how the trend in reactivity down the group depends on the outer shell electrons of the atoms. As you go down a group the atomic number increases.
Corner of the periodic table. On the other hand reactivity in non-metals increase further right down a period and further up a group. These demonstrations show the similarity of the physical and chemical properties of the alkali metals and the trend in reactivity down group 1 of the.
What happens when you go down a column on the periodic table. The melting point decreases as you go down the group from top to bottom. How do you determine chemical reactivity.
In association with Nuffield Foundation. Why does reactivity increase as you go down the periodic table. The valence electrons are less tightly.
For example barium has more activity than strontium or calcium. Up to 24 cash back Metals. This weaker attraction in the larger atoms makes it harder to gain electron.
Chemical Reactivity decrease as you go left to right of the periodic table.

A Visual Guide To Chemistry Glassware Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Labs Chemistry Practical

C10 2 Reactivity Series Chemistry Notes Calcium Magnesium Alkali Metal

Alkali Metals Alkali Metal Teaching Chemistry Apologia Chemistry
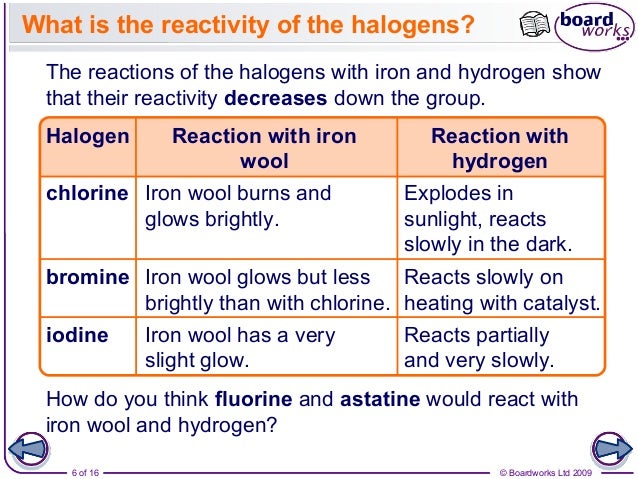
Comparing Halogen Reactivity Trends With Those Of The Alkali Metals Halogens Become Less Reactive Down The Chemistry Classroom High School Chemistry Chemistry

C10 2 Reactivity Series Chemistry Notes Calcium Magnesium Alkali Metal

Comparing Halogen Reactivity Trends With Those Of The Alkali Metals Halogens Become Less Reactive Down The Chemistry Classroom High School Chemistry Chemistry

Types Of The First Order Reaction Chemical Kinetics Reactions First Order

Effective Nuclear Charge Element Chemistry Electron Affinity

Periodic Trends In Ionic Radii Chemwiki Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Element Chemistry

Interactives The Periodic Table Groups Chemistry Classroom Science Chemistry Chemistry Notes

Compound Interest Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Education

Climate Zones Australia Maps Vocabulary Cards And Posters Tech Teacher Pto3 Climate Zones Australia Map Vocabulary Cards

Alkaline And Alkaline Earth Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Earth Alkaline

Drawing Bohr Models Using Periodic Trends Practice Teaching Resources Teaching Bohr Model Teaching Resources

Comments
Post a Comment